Designing Smart Automation Systems: Control Circuit Design Essentials
In the age of industrial transformation, automation has become a cornerstone of productivity and precision. Behind every automated process, from assembly lines to building management, Smart Automation Control Design. These circuits act as the nervous system of machines, enabling them to respond accurately to commands, environmental changes, and operational requirements.
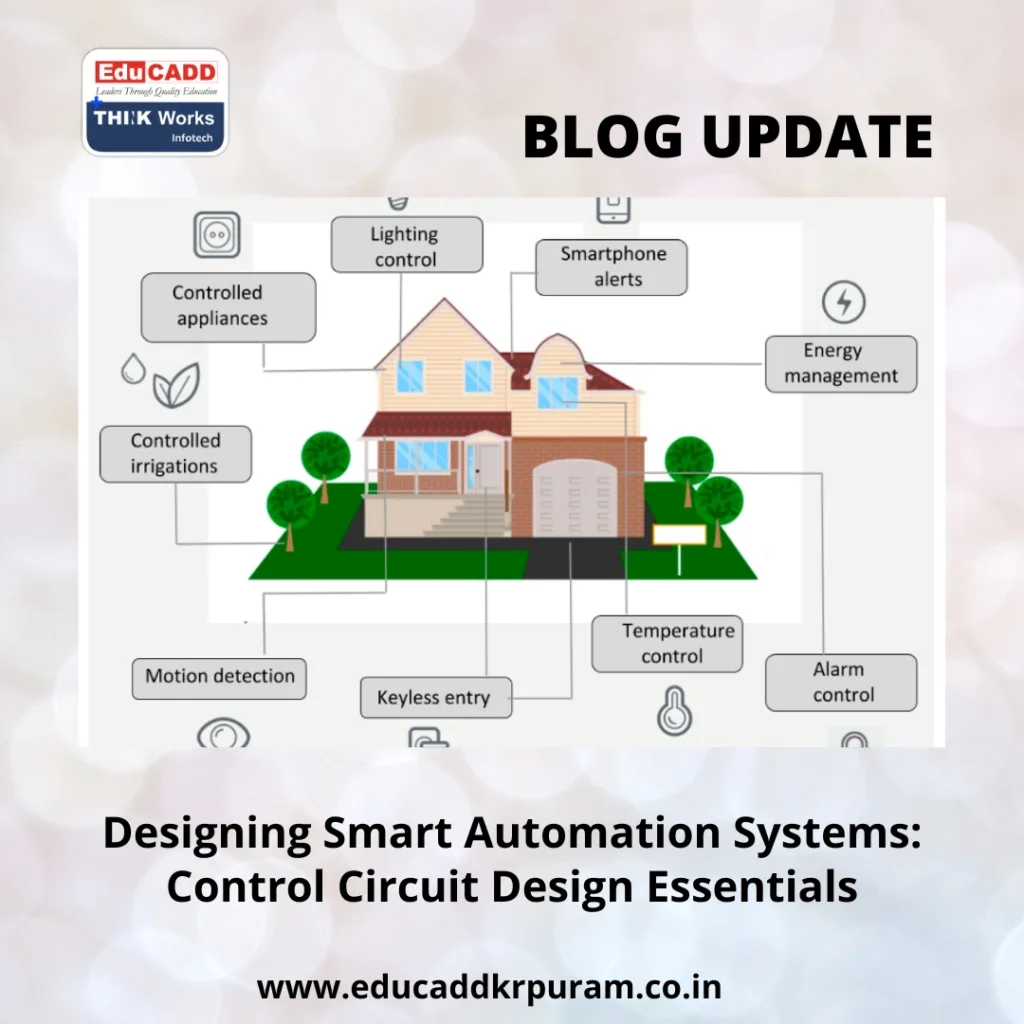
Smart Automation Control Design
Whether you are an aspiring engineer, a technician, or a student in industrial automation, understanding the intricacies of control circuits is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers principles, components, step-by-step design strategies, applications, emerging trends, and practical tips to help you create efficient and reliable automation systems.
1. Fundamentals of Control Circuit Design
Control circuit design for automation involves crafting electrical pathways that govern machine behavior. These circuits allow systems to function autonomously, responding to inputs and executing programmed instructions without constant human intervention.
Automation circuits are generally divided into two types:
-
Relay-Based Control Circuits – Using electromechanical relays, these circuits switch devices on and off. They are simple, cost-effective, and suitable for small-scale automation tasks.
-
PLC-Based Control Circuits – Programmable Logic Controllers provide high flexibility and scalability. They integrate easily with software, enabling complex industrial processes to run efficiently.
Modern automation systems also include sensors, timers, actuators, and safety devices. Sensors monitor environmental or operational conditions, timers ensure operations happen in sequence, and actuators carry out physical movements. Proper integration of these elements is essential to achieving a responsive and efficient system.
A well-designed control circuit not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves safety, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes human error.
2. Core Components of Automation Control Circuits
Creating an effective control circuit design for automation requires careful selection of components. Each component plays a specific role and contributes to the overall performance of the system.
Relays and Contactors
Relays control low-power devices, while contactors manage high-current equipment. They act as switches, ensuring devices operate safely and as intended.
Sensors
Sensors detect changes in temperature, pressure, motion, light, or other environmental conditions. These inputs allow circuits to respond dynamically, ensuring precise automation.
Actuators
Actuators convert electrical signals into mechanical movements. They perform tasks such as opening valves, moving robotic arms, or operating conveyor systems.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs serve as the brains of modern automation. They execute pre-programmed logic based on inputs and control multiple devices simultaneously, allowing complex processes to operate seamlessly.
Timers and Counters
Timers and counters control the sequence and duration of operations. They ensure machines operate in a precise, coordinated manner, preventing errors and collisions.
Other components include push buttons, limit switches, fuses, indicators, and overload protection devices. Combining these parts strategically is key to building a reliable and safe automation system.
Example: In an automated packaging system, sensors detect the position of packages, relays start motors, and actuators push items onto the conveyor. Proper component integration ensures smooth operation with minimal downtime.
3. Step-by-Step Approach to Designing Control Circuits
A structured approach is critical when designing control circuit design for automation. Following these steps guarantees functionality, safety, and scalability.
Step 1: Identify System Requirements
Begin by defining what the automation system needs to accomplish. Identify input and output devices, control logic, safety mechanisms, and operational goals. For example, a robotic sorting system may require sensors to detect items, relays to activate motors, and actuators to move objects into the correct bins.
Step 2: Create a Schematic Diagram
A detailed schematic diagram maps out all components, connections, and logical flow. It simplifies troubleshooting, ensures accuracy, and serves as a reference for installation and maintenance.
Step 3: Implement Sequential Control Logic
Sequential operation ensures that devices activate in the correct order. For instance, a conveyor motor should not start until safety gates are confirmed closed. Sequential control minimizes risks and prevents operational conflicts.
Step 4: Integrate Safety Measures
Incorporate safety devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, emergency stop switches, overload relays, and alarms. Safety is not optional—it protects both personnel and equipment.
Step 5: Test and Optimize
After construction, conduct functional testing under different operating conditions. Simulation software can also identify potential faults before implementing the physical system.
Step 6: Maintain Documentation
Keep detailed records of your design, components, wiring diagrams, and test results. Documentation facilitates troubleshooting, upgrades, and compliance with industrial standards.
By following these steps, engineers ensure their automation circuits are reliable, safe, and efficient.
4. Applications of Control Circuit Design in Industry
Control circuit design for automation is applied across diverse sectors, enhancing productivity, precision, and safety.
Manufacturing
Assembly lines, CNC machines, and robotic systems rely on control circuits to regulate motor speeds, sequences, and operations. Efficient control reduces downtime and improves production quality.
Building Management Systems
Automated HVAC, lighting, and security systems use control circuits to optimize energy consumption and enhance comfort. For instance, lighting circuits may adjust brightness based on occupancy sensors.
Water and Waste Management
Pumps, valves, and filtration systems operate automatically using control circuits. Timers and sensors ensure smooth operation and accurate resource management.
Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles integrate automated circuits for engine control, braking, airbag deployment, and safety systems. These circuits improve performance, reliability, and occupant protection.
Packaging and Material Handling
Conveyor belts, sorting machines, and labeling systems use control circuits for precise operation. Properly designed circuits reduce errors and increase throughput.
Case Study: In a beverage bottling plant, sensors detect bottle placement, relays start filling nozzles, and actuators move bottles along the conveyor. This automated system minimizes human involvement while increasing efficiency.
5. Emerging Trends in Control Circuit Design
The field of control circuit design for automation is evolving rapidly. Staying updated with emerging trends is essential for engineers and designers.
-
IoT-Enabled Automation: Circuits now integrate with IoT devices, enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time analytics.
-
Advanced PLCs and Microcontrollers: Modern controllers offer faster processing, enhanced memory, and software integration for complex automation tasks.
-
Energy-Efficient Designs: Engineers are increasingly focused on minimizing power consumption and reducing environmental impact.
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Artificial intelligence can optimize control circuits for adaptive operation and self-learning behavior.
-
Compact, Modular Designs: Miniaturized components allow more flexible, space-saving, and scalable automation systems.
The industry is moving toward smart, interconnected automation systems capable of adaptive control, fault detection, and cloud-based management. Engineers skilled in control circuit design are essential to implement these advanced systems successfully.
6. Practical Tips for Effective Control Circuit Design
To ensure high-quality automation circuits, follow these practical tips:
-
Prioritize Safety First: Always include protective devices like emergency stops, overload relays, and fuses.
-
Select High-Quality Components: Reliable relays, sensors, and PLCs reduce maintenance needs and prevent failures.
-
Use Simulation Tools: Test circuits virtually to identify potential faults before physical implementation.
-
Design Modular Systems: Modular layouts simplify troubleshooting, maintenance, and upgrades.
-
Document Everything: Maintain wiring diagrams, component specifications, and test results for reference.
-
Train Personnel: Well-trained operators ensure correct system usage, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Following these practices ensures that your control circuit design for automation is efficient, safe, and durable.
Conclusion
Smart Automation Control Design the backbone of modern industrial efficiency and reliability. From simple relay-based setups to sophisticated PLC and AI-driven systems, these circuits manage machines, improve productivity, and ensure safety.
Understanding the components, design principles, real-world applications, and emerging trends equips engineers to create innovative and dependable automation systems. By staying informed and applying practical techniques, professionals can develop future-ready circuits that meet industry demands while reducing errors and operational risks.
Investing time and effort in mastering control circuit design for automation opens the door to professional growth, advanced industrial applications, and significant contributions to technological progress.
