Transforming Building Design with Revit MEP for Drainage & HVAC Layouts
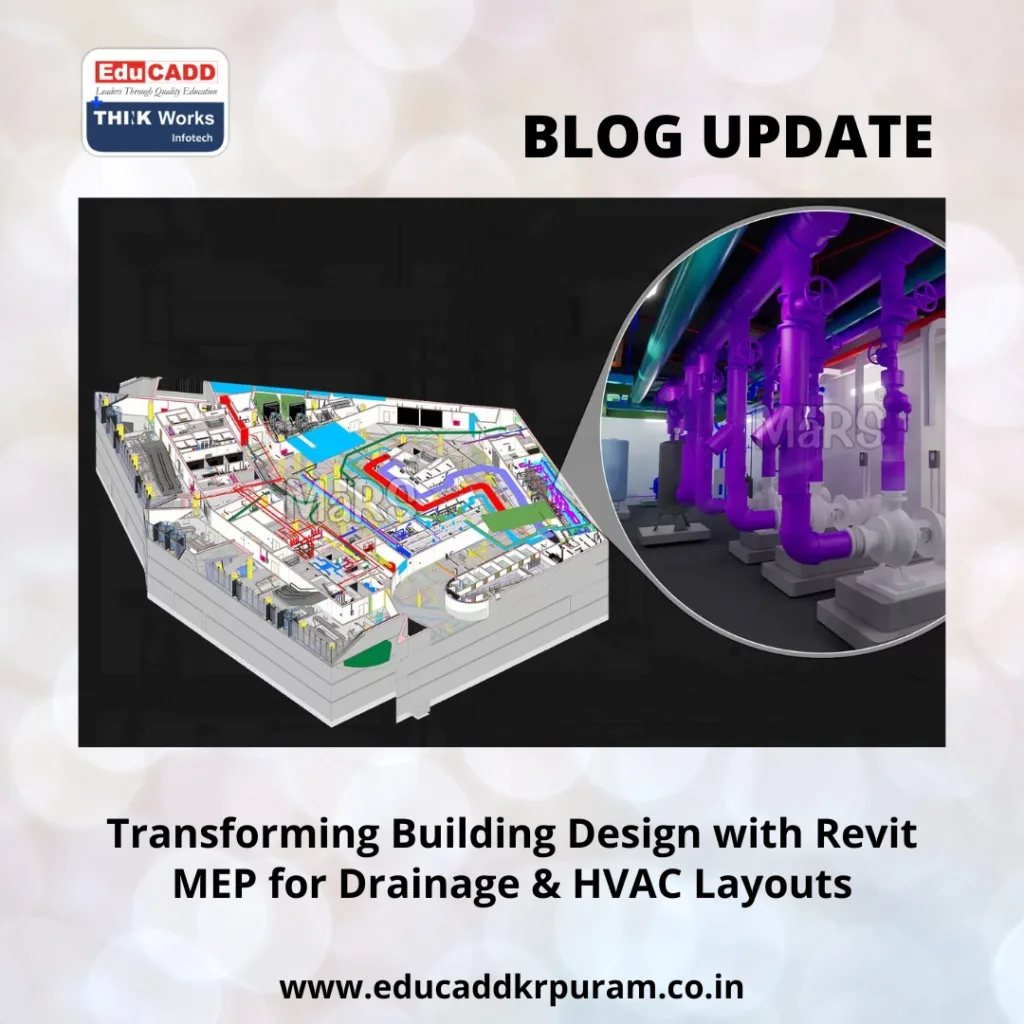
Modern construction projects demand precision, coordination, and efficiency in every phase of design. Among the most critical aspects are Revit MEP Layouts systems, particularly drainage and HVAC layouts. Effective planning of these systems ensures building safety, comfort, and long-term sustainability.
Traditional drafting methods often result in errors, miscommunication, and time-consuming corrections. Revit MEP, a Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, offers a dynamic solution by allowing engineers to create intelligent, data-driven models.
Revit MEP Layouts
This blog provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide to Revit MEP for Drainage & HVAC Layouts. It covers the entire workflow—from initial setup to advanced optimization—ensuring that both drainage and HVAC systems are functional, efficient, and ready for practical implementation.
Whether you are an MEP engineer, contractor, or design professional, following this guide will streamline your workflow, improve accuracy, and enhance collaboration across teams.
Why Revit MEP is Crucial for Drainage and HVAC Systems
MEP design is far more than drawing pipes or ducts; it requires precise integration of multiple systems into a single cohesive model.
Key Advantages of Revit MEP:
-
Accuracy and Coordination – Revit MEP automatically updates connected systems when changes are made, preventing costly errors.
-
3D Visualization – Stakeholders can view layouts in three dimensions, helping identify conflicts and optimize designs.
-
Team Collaboration – Engineers, architects, and contractors can work on a single shared model, reducing miscommunication.
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency – The software allows energy analysis, helping create eco-friendly HVAC solutions.
-
Documentation Automation – Revit generates schedules, reports, and construction drawings that stay updated with design changes.
For drainage and HVAC, even minor miscalculations can result in operational problems. Using Revit MEP ensures that every pipe, duct, and fitting is placed correctly and functions as intended.
Setting Up a Revit MEP Project
Before diving into drainage and HVAC layouts, proper project setup is critical. The setup phase lays the foundation for a smooth workflow and accurate model.
Step 1: Choose the Right Project Template
Templates contain predefined families, annotation styles, and system types. They help maintain consistency across multiple projects. Use an MEP template specific to drainage and HVAC for best results.
Step 2: Define Levels and Grids
Levels indicate vertical building positions, while grids provide horizontal alignment. Correct setup ensures that drainage pipes, HVAC ducts, and mechanical equipment align with structural and architectural elements.
Step 3: Import Architectural Models
Link the architectural model to your Revit project. This allows you to coordinate MEP systems with walls, floors, ceilings, and openings, avoiding clashes with other building components.
Step 4: Load MEP Families
Families are prebuilt components such as pipes, valves, ducts, diffusers, and fittings. Load families relevant to your project to match real-world specifications and reduce design errors.
Step 5: Set Project Units and Levels
Ensure that project units (mm, cm, or inch) match your standards. Proper level setup ensures accurate placement of drainage slopes and duct alignments.
Pro Tip: Establish view templates and filters for each system type. This makes model navigation easier and improves clarity for coordination.
Creating Efficient Drainage Layouts
Drainage systems handle wastewater safely and efficiently, preventing water damage and ensuring compliance with local building codes. Revit MEP streamlines drainage design through intelligent tools and automation.
Step 1: Define Pipe Types
Identify pipe material (PVC, HDPE, cast iron, copper) and assign diameters. Set up system classifications, such as sanitary, stormwater, or vent systems, to maintain clarity.
Step 2: Place Plumbing Fixtures
Position toilets, sinks, floor drains, and roof outlets. Revit automatically connects each fixture to the system, ensuring correct placement and alignment.
Step 3: Draw Pipes and Set Slopes
Create horizontal and vertical piping runs. Apply appropriate slopes for gravity-driven drainage systems, typically 1–2% for waste pipes.
Step 4: Add Fittings and Accessories
Connect pipes using elbows, tees, reducers, and cleanouts. Revit automatically adjusts fittings to match the pipe diameter and maintains system integrity.
Step 5: Validate System Connectivity
Run system checks to confirm all fixtures link correctly to drainage pipes. This ensures no leaks or misalignments during construction.
Step 6: Conduct Clash Detection
Identify conflicts between drainage pipes, HVAC ducts, and structural elements. Revit’s clash detection tool highlights potential problems for early resolution.
Advanced Tip: Use Revit’s slope analysis and routing preferences to optimize flow paths and reduce material usage.
Step-by-Step HVAC Layout Design
HVAC systems are critical for maintaining indoor air quality, temperature control, and occupant comfort. Revit MEP provides tools to plan efficient HVAC layouts while ensuring system performance.
Step 1: Load HVAC Equipment Families
Include air handling units (AHUs), chillers, pumps, diffusers, ducts, and grilles. Families should follow manufacturer specifications for accurate representation.
Step 2: Position Mechanical Equipment
Place equipment in mechanical rooms, ceiling voids, or designated shafts. Correct placement avoids clashes and allows easy maintenance access.
Step 3: Create Duct Systems
Draw supply, return, and exhaust ducts. Use Revit’s automated sizing based on airflow and pressure requirements. Apply duct insulation, if necessary, for energy efficiency.
Step 4: Add Air Terminals
Install diffusers, registers, and grilles at designated locations. Ensure proper connection to ducts and optimal airflow distribution.
Step 5: Assign System Properties
Set flow rates, pressures, fan types, and system classifications. Revit calculates performance parameters to ensure the HVAC system meets design standards.
Step 6: Analyze System Performance
Use Revit’s analysis tools to assess airflow, duct pressure drops, and energy consumption. Make adjustments to optimize efficiency and minimize energy waste.
Pro Tip: Use Revit’s space/zone-based HVAC design to automatically assign air distribution and calculate load requirements for each room.
Collaboration, Documentation, and Project Management
Revit MEP goes beyond design. Effective collaboration and documentation are essential for project success.
Coordinated Multi-Disciplinary Models
Link drainage and HVAC layouts with architectural, structural, and electrical models. This prevents conflicts and ensures that all building systems coexist harmoniously.
Automated Drawing Generation
Generate construction drawings, sections, elevations, and schedules directly from the model. Every change in the model updates all drawings automatically.
Clash Detection and Resolution
Coordinate with other disciplines to identify and resolve conflicts early. This reduces delays and rework during construction.
Cloud-Based Collaboration
Revit’s cloud workflows allow multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. This ensures everyone is aligned, regardless of location.
Pro Tip: Use shared parameters for all MEP components to maintain consistency across teams and projects.
Advanced Tips for Revit MEP Drainage and HVAC Projects
-
Use Routing Preferences: Customize pipe and duct routing rules to optimize layout efficiency.
-
Apply System Types Strategically: Classify pipes and ducts for better reporting and scheduling.
-
Leverage Templates and Libraries: Standardized templates save time and ensure consistency.
-
Perform Early Energy Analysis: Simulate HVAC performance to optimize equipment sizing and reduce operational costs.
-
Document for Construction: Include fabrication details, installation instructions, and material lists directly from Revit.
Future Trends in MEP Design
The construction industry is moving toward smarter, data-driven, and energy-efficient designs. Revit MEP evolves alongside these trends:
-
Automation and AI Integration: Automate repetitive tasks, reducing design time and errors.
-
Sustainability Focus: Analyze HVAC efficiency and water usage to reduce energy consumption.
-
IoT Integration: Connect MEP systems to sensors for smart building management.
-
Cloud Collaboration: Enable remote teamwork, allowing real-time updates and model access.
Adopting Revit MEP positions firms to meet the increasing demand for high-performance, sustainable, and error-free building designs.
Conclusion
Revit MEP Layouts – A Step-by-Step Guide transforms MEP design from manual drafting to a fully integrated, intelligent process. From initial project setup to advanced system analysis, Revit ensures that every pipe, duct, and fixture is placed accurately.
Engineers can streamline workflows, reduce errors, and create optimized, energy-efficient systems ready for construction. By adopting Revit MEP, professionals not only improve project quality but also gain a competitive edge in modern construction.
