The Logic Blueprint: Understanding Activity Network Diagrams for Smarter Project Planning
Projects rarely fail because people don’t work hard — they fail because tasks are poorly organized. Without a clear plan, dependencies get missed, deadlines slide, and resources are wasted. The Activity Network Diagram Guide fixes this problem by making the project’s logic visible.
It’s more than just boxes and arrows. It’s a thinking tool that helps you see exactly what needs to happen, in what order, and how long it will take. Whether you’re running a construction project, developing software, or planning an event, mastering this diagram can help you keep your project under control.
Activity Network Diagram Guide
In this guide, we’ll break down what the Activity Network Diagram is, how it works, how to create one, why it’s useful, and where it’s applied in real life.
1. Defining the Activity Network Diagram
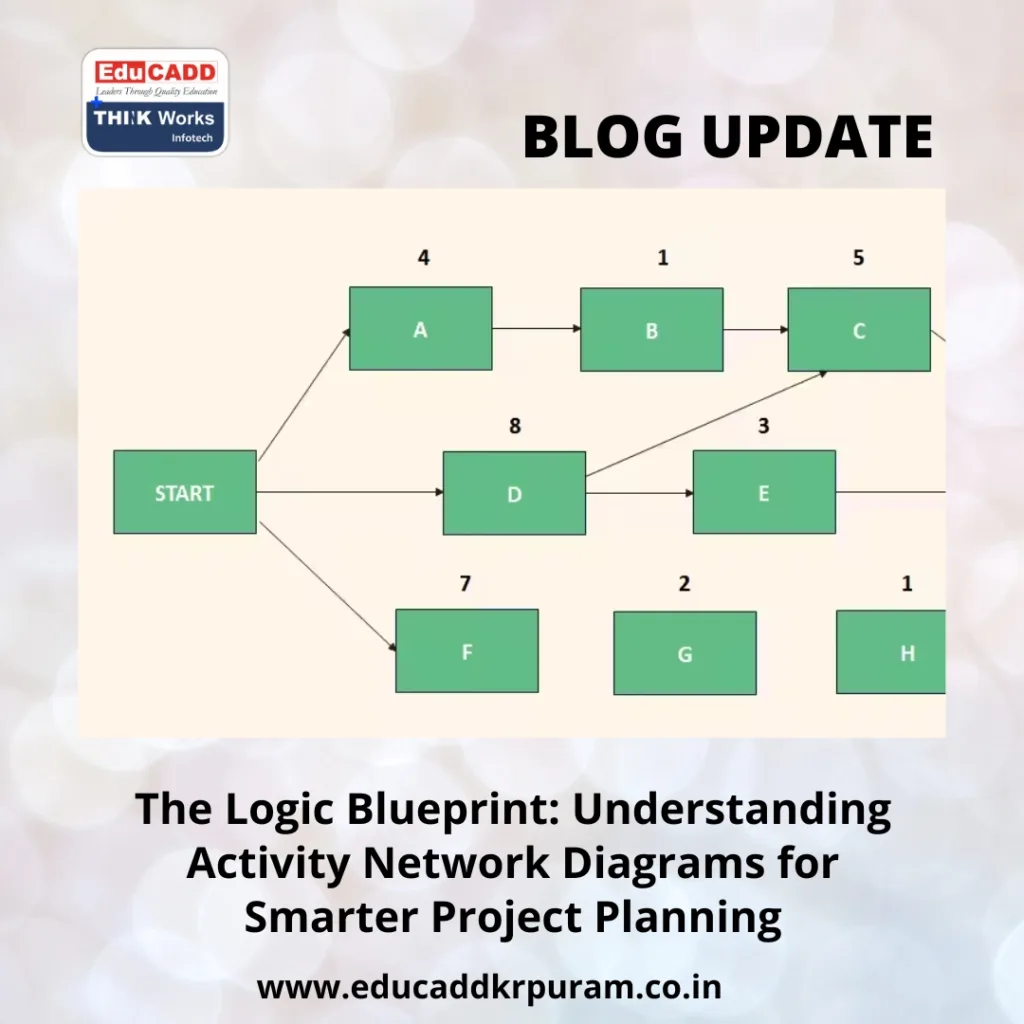
An Activity Network Diagram is a visual representation of a project’s workflow. Activities are displayed as nodes, and arrows show the sequence and dependencies between them.
It differs from a simple list because it reveals how tasks connect and which ones depend on others. The diagram also highlights the critical path — the series of tasks that determine the shortest possible time to complete the project.
For example, in a building project, you can’t install windows before the walls are built. The diagram ensures such logical sequences are clearly mapped out so no step is overlooked.
2. The Logical Foundation Behind It
At its heart, the Activity Network Diagram follows a simple but powerful logic:
-
Some tasks must be completed before others can start.
-
Certain tasks can run in parallel to save time.
-
Delays in critical tasks will delay the entire project.
This logic creates a flow that starts with activities with no dependencies, then moves through connected tasks until the project is complete. By mapping these relationships, managers can anticipate roadblocks and adjust before problems occur.
This isn’t just theory. It’s the same logic engineers, event managers, and software developers use to keep complex projects running smoothly.
3. Steps to Create Your Own Activity Network Diagram
Building an Activity Network Diagram is straightforward if you follow a structured approach.
Step 1: Identify All Project Tasks
Write down every activity, big or small. Missing even one task can distort the plan.
Step 2: Determine Dependencies
Ask which tasks depend on others to be completed first.
Step 3: Estimate Duration
Assign realistic time estimates to each task to create an accurate schedule.
Step 4: Draw the Diagram
Represent tasks as nodes and connect them with arrows showing dependencies. Arrange them from the project’s start to its end.
Step 5: Find the Critical Path
Highlight the longest chain of dependent activities. This path determines the minimum time to finish the project.
Following these steps gives you a diagram that not only organizes the work but also reveals where you must focus to stay on schedule.
4. Benefits of Using an Activity Network Diagram
The Activity Network Diagram offers several advantages that directly improve project outcomes.
Clear Visualization
It transforms a list of tasks into a logical, easy-to-read flow.
Improved Communication
A single diagram can be shared with the entire team, ensuring everyone understands the plan.
Risk Reduction
By showing dependencies, it’s easier to identify points where delays are most likely to occur.
Efficient Time and Resource Use
Knowing which tasks can run in parallel prevents resource bottlenecks.
Better Decision-Making
Managers can see where to allocate extra effort or adjust schedules to keep projects on track.
These benefits make the diagram a go-to method in industries that depend on accurate timelines.
5. Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
The Activity Network Diagram is widely used because it adapts to different project types.
Construction
From site preparation to finishing touches, construction requires a logical order. Diagrams ensure each phase starts and ends on time.
Software Development
Coding, testing, and deployment have dependencies that must be tracked to avoid delays.
Event Planning
In organizing events, tasks like venue booking, catering, and invitations need careful sequencing.
Manufacturing
Production lines benefit from knowing exactly when each stage must happen to maintain efficiency.
Research Projects
In R&D, certain experiments or data collection phases must happen before analysis.
Across these industries, the diagram works as a universal language for project logic.
Conclusion: Turning Plans into Results
The Activity Network Diagram isn’t just about drawing shapes — it’s about applying logic to your project from start to finish. By making dependencies visible, it ensures that every task happens in the right order and on time.
When you master this tool, you move beyond guesswork. You can see the path ahead, prepare for challenges, and deliver results with confidence.
