DevOps Uncovered: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals
In today’s rapidly evolving technology landscape, delivering software quickly and reliably has become a critical business requirement. Traditional workflows often create bottlenecks, miscommunications, and delays between development and operations teams. DevOps IT Professional Guide bridges this gap, fostering collaboration, automation, and efficiency.
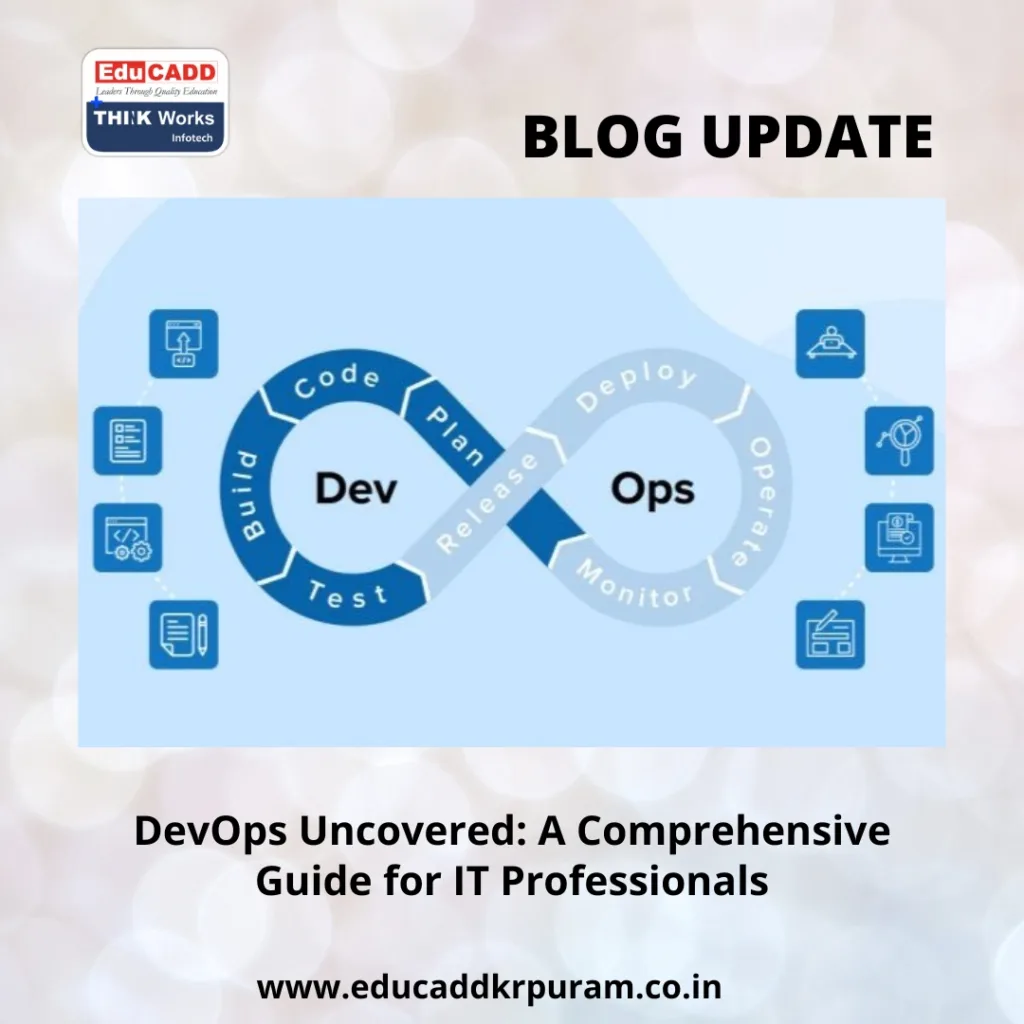
DevOps IT Professional Guide
This guide, DevOps Uncovered: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals, explores the principles, tools, and career benefits of DevOps. By following this roadmap, IT professionals can gain practical insights to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and advance their careers.
1. Understanding DevOps: Definition and Importance
At its core, DevOps combines development (Dev) and operations (Ops) into a unified approach that emphasizes collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement. Traditionally, development teams focused solely on coding while operations teams handled deployment and maintenance. This separation often caused delays and errors.
DevOps transforms this dynamic by enabling developers and operations teams to work together seamlessly. Automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery are central to this approach, leading to faster software releases, fewer errors, and improved user satisfaction.
Key benefits of DevOps for IT professionals:
-
Accelerated software deployment
-
Improved team collaboration
-
Enhanced reliability and scalability
-
Reduced downtime and operational issues
-
Higher customer satisfaction
In essence, DevOps is not just a methodology—it is a mindset that reshapes how IT teams deliver value.
2. Core Principles of DevOps
To effectively implement DevOps, IT professionals must understand its foundational principles. These principles guide teams in improving workflows, enhancing collaboration, and ensuring high-quality software delivery.
2.1 Collaboration and Open Communication
DevOps encourages breaking down traditional silos. Developers, testers, and operations teams work in close coordination. Open communication ensures issues are identified and resolved promptly.
2.2 Automation Across the Workflow
Automation reduces manual errors and accelerates processes. Tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Kubernetes automate testing, deployment, and infrastructure management.
2.3 Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD pipelines streamline the integration of code changes and automate deployments. Continuous integration ensures smooth merging of new code, while continuous delivery enables rapid and reliable releases.
2.4 Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
Monitoring systems detect issues in real-time. Feedback loops from users and internal teams drive ongoing improvements, ensuring applications remain robust and responsive.
2.5 Security as a Core Component
Modern DevOps integrates security from the start, known as DevSecOps. Automated security checks in pipelines prevent vulnerabilities and protect applications.
By following these principles, teams can deliver high-quality software more efficiently and consistently.
3. Essential DevOps Tools and Technologies
Tools play a critical role in implementing DevOps. Mastery of these tools is essential for IT professionals aiming to thrive in DevOps roles.
3.1 Version Control Systems
Git, along with platforms like GitHub or GitLab, allows teams to track changes, collaborate efficiently, and manage code versions effectively.
3.2 CI/CD Platforms
Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitLab CI automate building, testing, and deployment processes, reducing manual work and speeding up release cycles.
3.3 Configuration Management
Ansible, Puppet, and Chef maintain consistent configurations across servers, ensuring stability across development, testing, and production environments.
3.4 Containerization and Orchestration
Docker provides containerized environments, while Kubernetes orchestrates containers at scale for easier deployment and management.
3.5 Cloud Platforms
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable infrastructure and DevOps services, supporting automated pipelines and monitoring.
3.6 Monitoring and Logging Tools
Grafana, Prometheus, and the ELK Stack help track performance, detect errors, and provide actionable insights for continuous improvement.
3.7 Collaboration Tools
Jira, Slack, and Microsoft Teams streamline task management and team communication, essential for smooth DevOps workflows.
Mastering these tools allows IT professionals to implement DevOps practices effectively, enhancing productivity and reliability.
4. Advantages of DevOps for IT Professionals
DevOps offers numerous career benefits, from enhancing skills to creating better job opportunities.
4.1 Increased Employability
Organizations across industries actively seek skilled DevOps professionals. Demand continues to grow globally, offering ample opportunities.
4.2 Stronger Collaboration Skills
DevOps promotes teamwork and communication, helping IT professionals solve problems effectively and work in cross-functional environments.
4.3 Exposure to Cutting-Edge Tools
Professionals gain hands-on experience with automation, containerization, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud services. These skills are highly valued in the industry.
4.4 Enhanced Productivity
Automation reduces repetitive tasks, allowing IT professionals to focus on innovation and strategic initiatives.
4.5 Career Growth and Competitive Salaries
DevOps expertise opens doors to roles such as Site Reliability Engineer, DevOps Architect, and Cloud Engineer, often accompanied by higher pay.
By mastering DevOps, IT professionals can advance their careers and increase their impact on organizational success.
5. How to Begin Your DevOps Journey
Starting a DevOps career requires a structured approach. Here are the key steps for IT professionals:
5.1 Understand the Basics
Learn the core concepts, principles, and benefits of DevOps through online courses, blogs, and guides.
5.2 Gain Hands-On Experience with Tools
Practice using Git, Docker, Jenkins, and Kubernetes through personal projects or lab environments.
5.3 Learn Cloud Platforms
Familiarity with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud is essential, as most DevOps workflows are cloud-based.
5.4 Develop Scripting Skills
Languages like Python, Bash, or Go help automate tasks, improving efficiency and reducing manual work.
5.5 Work on Real Projects
Contribute to open-source projects or implement your own CI/CD pipelines to gain practical experience.
5.6 Stay Updated
Follow industry news, attend webinars, and join communities to keep up with the fast-evolving DevOps landscape.
These steps build a strong foundation for a successful career in DevOps.
Conclusion: Embrace DevOps for Career Success
DevOps IT Professional Guide is not just a methodology—it is a transformative approach that integrates development, operations, and security. By adopting DevOps principles, IT professionals can deliver software faster, more reliably, and with greater collaboration.
DevOps Uncovered: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Professionals has highlighted the principles, tools, benefits, and career pathways. Embracing DevOps ensures you stay competitive, gain valuable skills, and unlock a rewarding career in one of the fastest-growing fields in IT.
